The main parts of a sentence are the subject and the predicate. These two components work together to form a complete sentence.
Parts Of A Sentence: Subject And Predicate
Subject:
The subject is the noun or pronoun that performs the action or is being described in the sentence. It is typically the “who” or “what” that the sentence is about. Examples: “she,”, “cat”, “Abir and Amina”, “and book”.
Examples of the subject:
- Raihan runs.
- The car needs a new battery.
- She is studying for her final exams.
- The cat is sleeping on the windowsill.
- The children were playing in the park.
- The baby is sleeping peacefully in her crib.
- My mother baked a delicious cake for me.
- My friend and I went to the field yesterday.
- The computer crashed during the presentation.
- Kabir and his cat run on the field every morning.
Predicate:
The predicate is part of the sentence that includes the verb and provides information about the subject. It usually tells what the subject is doing or what is happening. Examples: “runs”, “eats”, “is reading”, and “has been playing”.
Examples of the predicate:
- Raihan runs.
- The car needs a new battery.
- She is studying for her final exams.
- The cat is sleeping on the windowsill.
- The children were playing in the park.
- The baby is sleeping peacefully in her crib.
- My mother baked a delicious cake for me.
- My friend and I went to the field yesterday.
- The computer crashed during the presentation.
- Kabir and his cat run on the field every morning.
Parts Of A Sentence: Subject And Predicate
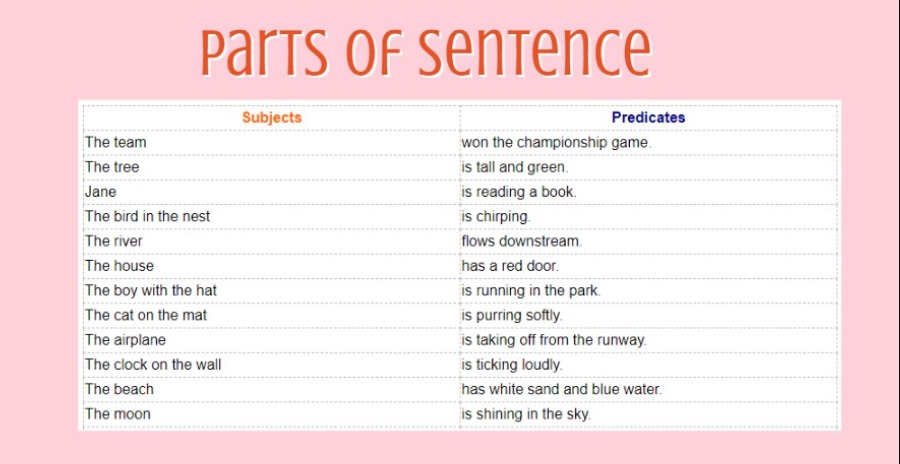
More Examples of Subjects and Predicates In a Table:
| Subjects | Predicates |
| The team | won the championship game. |
| The tree | is tall and green. |
| Jane | is reading a book. |
| The bird in the nest | is chirping. |
| The river | flows downstream. |
| The house | has a red door. |
| The boy with the hat | is running in the park. |
| The cat on the mat | is purring softly. |
| The airplane | is taking off from the runway. |
| The clock on the wall | is ticking loudly. |
| The beach | has white sand and blue water. |
| The moon | is shining in the sky. |
| The cake on the table | is chocolate flavored. |
| The student | is writing an essay. |
| The thunderstorm | is rumbling outside. |
| The car in the garage | is being repaired. |
| The ocean | is vast and mysterious. |
| The phone | is ringing loudly. |
| The elephant | is trumpeting loudly. |
| The boat on the lake | is sailing smoothly. |
| The rainbow | is spanning across the sky. |
| The runner | is sprinting to the finish line. |
| The flowers in the vase | are wilting. |
| The airplane | is taking off. |
| The baby | is crawling on the floor. |
| The airplane | is landing on the runway. |
| The teacher | is writing on the whiteboard. |
| The butterfly | is fluttering its wings. |
| The fire | is crackling in the fireplace. |
| She | reads a book. |
| The car | needs repairs. |
| We | are cooking dinner. |
| The students | are studying. |
| The rain | stopped. |
| The train | is arriving. |
| The baby | is crawling. |
Parts Of A Sentence
Apart from the subject and predicate, which are the two main parts of a sentence, there are several other parts that may be present in a sentence. These include:
1. Noun: A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. It can function as the subject, object, or complement in a sentence. Example: The cat is sleeping.
2. Pronoun: A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. It can function as a subject, object, or complement in a sentence. Example: They are going to the park.
3. Adjective: An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun. It provides more information about the noun, such as its size, color, shape, or quality. Example: The red car is fast.
4. Verb: A verb is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being. It is the main component of the predicate and indicates what the subject is doing or what is happening in the sentence. Example: She is reading a book.
5. Adverb:
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. It typically provides information about how, when, where, or to what extent the action or state is happening. Example: He runs quickly.
6. Preposition: A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. It typically indicates location, direction, time, or manner. Example: She walked across the bridge.
7. Conjunction: A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. It can be used to join two or more nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, or sentences. Example: He likes both chocolate and vanilla.
8. Interjection: An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a strong feeling or reaction. It is usually used to convey emotions, such as surprise, joy, or anger. Example: Wow, what a beautiful day!
Understanding the concept of subjects and predicates is essential for constructing grammatically correct sentences. The subject, being the main noun or pronoun that performs the action or states of being, and the predicate, being the verb or verb phrase that tells what the subject is doing or what is happening, work together to form the foundation of sentence structure.
So, whether you are writing an essay, a report, or a simple email, always keep in mind the importance of subjects and predicates in constructing meaningful and grammatically sound sentences. Use them correctly to make your ideas clear and persuasive, and watch your writing soar to new heights of clarity and effectiveness.
Read More:
Subject Verb Agreement Examples
Leave a Reply