In computing, memory plays a crucial role in storing and accessing data. There are two common types of memory that you might have come across: RAM (random access memory) and ROM (read-only memory). Both of these are essential components of electronic devices; they have distinct characteristics and serve different purposes.
What is RAM?
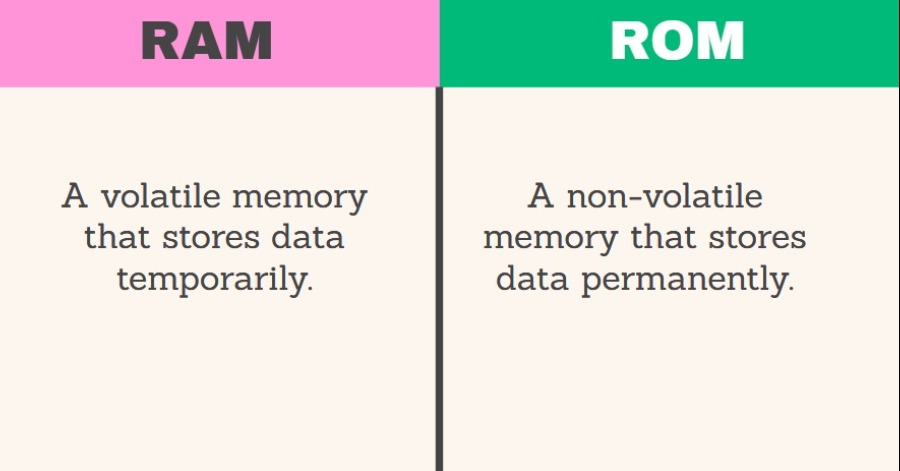
RAM, or random access memory, is a type of volatile memory that acts as the main memory for electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. RAM allows for rapid read and write operations, enabling the quick retrieval and modification of data. It serves as a temporary workspace where the operating system, software applications, and data reside during active use.
One of the key characteristics of RAM is its volatility. This means that RAM requires a continuous power supply to retain data. As soon as the power is disconnected, the contents stored in RAM are lost. Consequently, RAM is considered temporary storage, where data is transiently held while the system is operational. When you turn off your device, the data in RAM is wiped clean, ready for a fresh start upon the next boot.
What is ROM?
ROM, or read-only memory, is a non-volatile memory that stores data permanently. ROM is primarily used for reading data and does not allow for modification or overwriting of its contents. It contains firmware, boot loaders, and software instructions that are crucial for the operation of electronic devices.
Unlike RAM, which is designed for dynamic data storage, ROM is used to store information that remains intact even when the device loses power. This makes ROM an essential component for preserving critical data, system configurations, and pre-programmed instructions that are essential for the device’s functionality. ROM is often found in embedded systems, gaming consoles, smartphones, and other electronic devices.
Difference between RAM and ROM in a tabular form
| Features | RAM | ROM |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A volatile memory that stores data temporarily | A non-volatile memory that stores data permanently |
| Read/Write | Read and write operations | Read-only, cannot be modified |
| Data Retention | Requires power to retain data | Retains data even without power |
| Usage | Main memory for running programs and storing data | Stores firmware, boot loaders, and software instructions |
| Capacity | Typically larger in capacity than ROM | Smaller capacity compared to RAM |
| Types | DRAM (Dynamic RAM), SRAM (Static RAM) | PROM (Programmable ROM), EPROM, EEPROM, Flash memory |
| Speed | Faster access and data retrieval | Slower access compared to RAM |
| Cost | Relatively cheaper | Costlier than RAM |
| Erasability | Not erasable | Some types can be erased and reprogrammed |
| Examples | DDR4, DDR3, SRAM | PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, Flash memory |
Difference between RAM and ROM
More information about RAM
RAM, or random access memory, is a type of computer memory used as the main memory in electronic devices. It is a volatile memory that requires a constant power supply to retain data. RAM allows for fast data storage and retrieval, making it ideal for active use. It offers quick read-and-write operations, facilitating multitasking and smooth application execution. RAM capacities vary depending on the device, ranging from gigabytes to terabytes. However, it is important to note that RAM is temporary storage, as data is lost when power is disconnected.
More information about ROM
ROM, or read-only memory, is a type of computer memory that stores data permanently and cannot be modified easily. Unlike RAM, ROM is non-volatile and retains its contents even when the power is disconnected. It is used to store firmware, boot loaders, and software instructions crucial for device operation. ROM is read-only and comes in different types, such as PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, and flash memory. These variations allow for programming, erasing, and reprogramming of the memory.
FAQs: Difference Between RAM And ROM
1. What is the main difference between RAM and ROM?
Answer: RAM (Random Access Memory) is a type of volatile memory used for the temporary storage of data during active use, while ROM (Read-Only Memory) is a non-volatile memory that stores data permanently and cannot be easily modified.
2. Can data be modified in RAM?
Answer: Yes, data stored in RAM can be modified and updated. It allows for both read and write operations, making it suitable for dynamic data storage.
3. Can data be modified in ROM?
Answer: No, data stored in ROM cannot be easily modified. It is typically programmed during the manufacturing process and remains static. However, certain types of ROM, such as EPROM and EEPROM, can be erased and reprogrammed using specific methods.
4. Which type of memory retains data when power is disconnected?
Answer: ROM retains data even when the power supply is disconnected because it is non-volatile. On the other hand, RAM is volatile memory and requires a continuous power supply to retain data.
5. What is the purpose of RAM?
Answer: RAM serves as the main memory in electronic devices and is used for running programs, storing active data, and providing temporary storage for quick access and manipulation by the processor.
6. What is the purpose of ROM?
Answer: ROM is primarily used to store firmware, boot loaders, and software instructions that are essential for the operation of electronic devices. It contains pre-programmed data that remains intact even without a power supply.
7. Which memory type is faster: RAM or ROM?
Answer: RAM is faster than ROM when it comes to data access and retrieval. RAM allows for quick read and write operations while accessing data from ROM is generally slower.
8. Can ROM be erased and reprogrammed?
Answer: Certain types of ROM, such as EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) and EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), can be erased and reprogrammed using specific methods. However, most types of ROM are not designed for frequent erasure and reprogramming.
9. How is the capacity of RAM and ROM different?
Answer: RAM generally has a larger capacity compared to ROM. RAM capacities can range from gigabytes (GB) to terabytes (TB), depending on the device and its intended use. ROM, on the other hand, typically has a smaller capacity compared to RAM.
10. What are some examples of RAM and ROM?
Answer: Examples of RAM include DDR4, DDR3, and SRAM. Examples of ROM include PROM (Programmable ROM), EPROM, EEPROM, and flash memory, which are commonly found in various electronic devices.
Read More:
Difference between power and authority
Difference between plant and animal
Leave a Reply